ON
o
|
|
|||
|
PNL Volume 18 1986 RESEARCH REPORTS
|
59
|
||
|
|
|||
|
EFFECT OF GIBBERELLIN TREATMENT ON THE EXPRESSIVITY OF MUTANT GENES IN
HOMO- AND HETEROZYGOUS CONDITION
Sidorova, K. K. Institute of Cytology & Genetics, Novosibirsk, USSR
A mutant allele, when present in a heterozygous condition along with
the wildtype allele at the same locus, may exert an influence ranging from
a very small effect (detectable only by special means) to co-dominance to
overdominance (i.e. monogenic heterosis). I studied this question by
measuring the influence of gibberellin on a series of mutants, when the
mutants were in either the homozygous or heterozygous condition.
In this experiment ten mutant lines were used, all ten having been
induced in the dwarf pea 'Polzunok'. The mutants were crossed with the
initial form. Both F1 and F2 were studied. All were found to be recessive
nuclear mutations, monohybrid segregations being observed in F2.
Seedlings of the initial form, mutants, and heterozygotes for mutant
genes were treated at the 3-4 node stage with gibberellin (50 mg/1 solution
gibbersib). Two treatments were made, three days apart. The solution was
placed on the growing point of a stem. Fifty plants of each variant were
studied under field conditions.
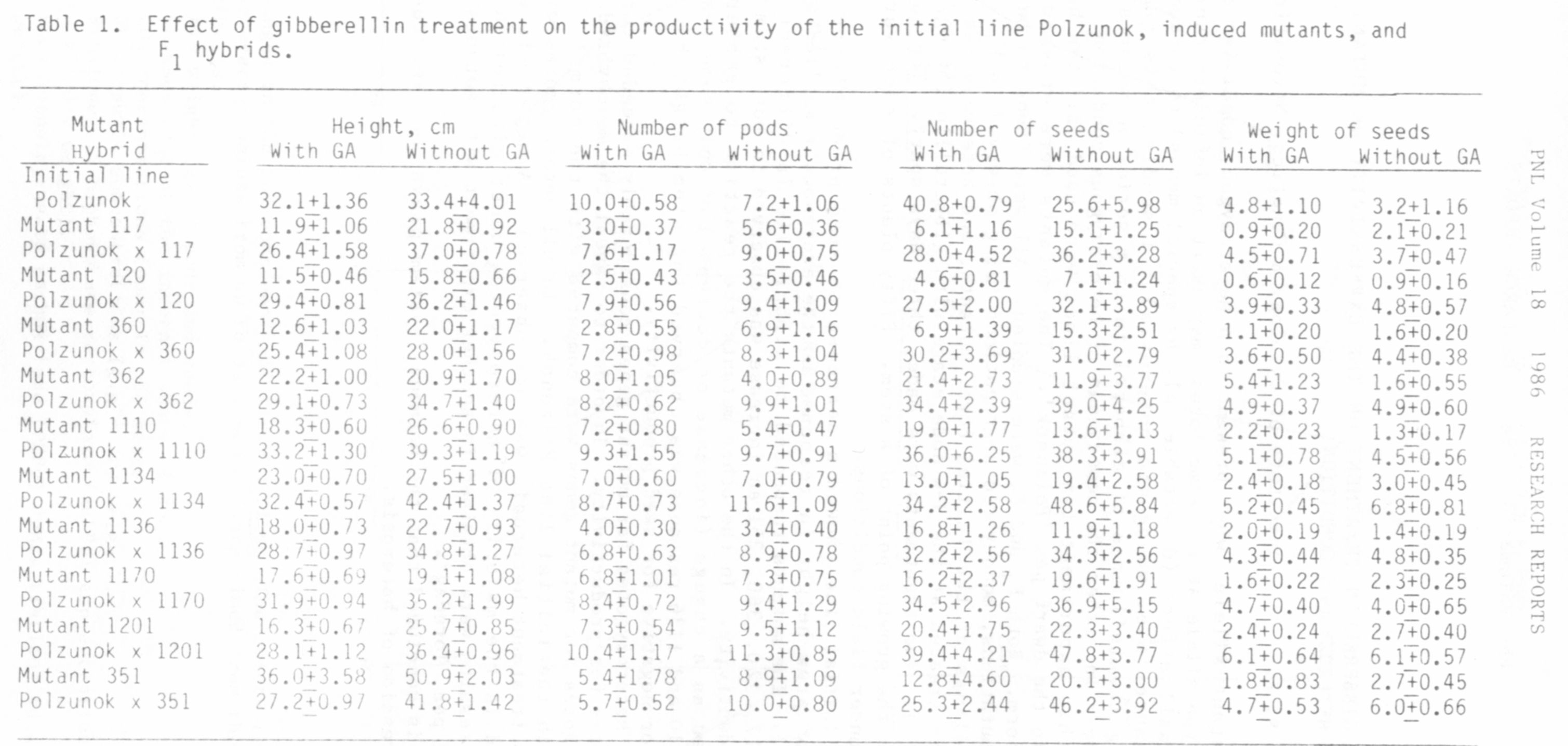
The initial line showed a decrease of seed productivity but not a
change of stem height in response to the exogenously applied gibberellin
(Table.1). The mutants responded to gibberellin in different ways. In
lines 117, 120, 360, 351 an increase was observed in both stem height and
seed productivity. In the other mutants the reaction to gibberellin was
expressed as a change (increase or decrease) of only some features. In
lines 1110 and 1136 response was observed for stem height but they were
neutral or negative for seed productivity.
All heterozygotes for mutant genes considerably exceeded corresponding
homozygotes for productivity. In order to reveal the monohybrid heterosis,
heterozygotes for mutant genes were compared with the normal homozygote,
i.e. with the initial line Polzunok. In all heterozygotes without gib-
berellin treatment heterosis was not observed. A heterosis effect was
observed in the majority of heterozygotes under gibberellin treatment.
Similar results were obtained in another experiment with mutants induced in
the tall pea 'Torsdag'.
It is concluded that the hormonal system plays an important role in
the expression of heterosis.
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
||
|
ON
o
|
||
|
|
||
 |
||
|
|
||