Pisum Genetics Volume 27 1995 Research Reports page 22
Linkage of gene chi-33 on linkage
group VI
Swiecicki, W.K. Institute of Plant Genetics, Polish Academy of Sciences
and Kruszka, K. Strzeszynska 34, Poznan 60-479, Poland
The spontaneous chlorotica mutation chi-33 (Wt11019) shows clear expression at the seedling stage except under greenhouse conditions (1). A preliminary linkage test (1) indicated significant linkage between chi-33 and linkage group VI marker Pl (29 cM) but linkage with wlo on this chromosome was not significant.
To locate chi-33 more precisely, we crossed Wt11019 with tester line Wt11777 which carries four group VI markers Pl, Arg, wlo and art-1. In the F2, chi-33 and the four markers all showed normal monohybrid segregation (Table 1). Dihybrid segregation analyses (Table 1) provided strong evidence of linkage between chi-33 and markers Arg (P<0.0001, 13.6 cM) and Pl (P<0.0001, 16.7 cM) but only weak evidence of linkage between chi-33 and markers wlo (P<0.01, cM 25.4) and art-1 (P<0.05, 29.7 cM). Together with the previous data (1), these results indicate chi-33 is located in the linkage group VI and closer to Pl than wlo. The data in Table 1 suggest the following arrangement of loci:
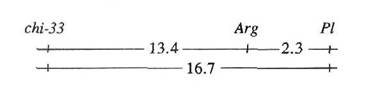
Table 1. Monohybrid (a) and dihybrid (b) segregation
in the F2 population of the cross
K. 1317 = Wt 11019 (chi-33, arg, pl, Art-1, Wlo) x Wt 11777 (Chi-33, Arg, Pl, art-1, wlo).
|
(a) |
Phenotype* |
Chi-sq. (3:1) |
||||||||
|
Locus |
D |
R |
Total |
|||||||
|
Chi-33 |
100 |
30 |
130 |
0.26 |
||||||
|
Arg |
98 |
32 |
130 |
0.01 |
||||||
|
Pl |
96 |
31 |
127 |
0.02 |
||||||
|
Art-1 |
102 |
27 |
129 |
1.14 |
||||||
|
Wlo |
96 |
34 |
130 |
0.09 |
||||||
|
(b) |
Phenotype* |
Joint Chi-sq. |
Recomb fract. |
SE |
||||||
|
Loci |
DD |
DR |
RD |
RR |
Total |
|||||
|
Chi-33/Arg |
91 |
9 |
7 |
23 |
130 |
56.9 |
13.6 |
3.2 |
||
|
Chi-33/Pl |
88 |
11 |
8 |
20 |
127 |
43.0 |
16.7 |
3.7 |
||
|
Arg/Pl |
95 |
2 |
1 |
29 |
127 |
111.1 |
2.3 |
1.3 |
||
|
Chi-33/Art-1 |
75 |
25 |
27 |
2 |
129 |
4.4 |
29.7 |
7.9 |
||
|
Chi-33/Wlo |
68 |
32 |
28 |
2 |
130 |
7.7 |
25.4 |
8.1 |
||
*D = homozygous dominant + heterozygous; R = homozygous recessive
1. Apisitwanich, S. and Swiecicki, W.K. 1993. Pisum Genetics 25:17.